What is the Loan to Debt Ratio for a Mortgage?
| Heading | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Explanation of loan to debt ratio for mortgages and its importance |
| Understanding Loan to Debt Ratio | Defining the loan to debt ratio, its calculation, and significance |
| Importance of Loan to Debt Ratio | Discussing why lenders consider loan to debt ratio during mortgage approval |
| Factors Influencing Ratio | Explaining factors affecting the loan to debt ratio |
| Ideal Loan to Debt Ratio | Describing the recommended ratio for mortgage applicants |
| Calculating Loan to Debt Ratio | Step-by-step guide on calculating loan to debt ratio |
| Tips for Improving Ratio | Providing tips to improve the loan to debt ratio |
| Risks of High Ratio | Explaining the risks associated with a high loan to debt ratio |
| FAQs | Answering frequently asked questions about loan to debt ratio for mortgages |
| Conclusion | Summarizing key points and importance of maintaining a healthy ratio |
Introduction What is the Loan to Debt Ratio for a Mortgage
When delving into the world of mortgages, understanding the loan to debt ratio becomes paramount. This crucial metric holds significant weight in the eyes of lenders, determining the feasibility of extending a mortgage to an applicant. Let’s delve deeper into what exactly the loan to debt ratio entails and why it matters.
Understanding Loan to Debt Ratio
Loan to Debt Ratio: A Critical Metric for Mortgage Approval
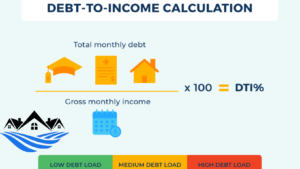
The loan to debt ratio, often referred to as the debt-to-income ratio (DTI), represents the proportion of a borrower’s monthly income that goes toward debt repayment, including mortgage payments. Lenders use this metric to assess an individual’s ability to manage additional debt responsibly.

Importance of Loan to Debt Ratio
Why Lenders Care About Your Loan to Debt Ratio
Lenders view the loan to debt ratio as a reflection of a borrower’s financial health and risk level. A lower ratio indicates that an individual has more disposable income after meeting debt obligations, making them a less risky investment for lenders. Thus, maintaining a healthy loan to debt ratio is crucial for securing favorable mortgage terms.
Factors Influencing Ratio
What Factors Influence Your Loan to Debt Ratio?
Several factors contribute to the loan to debt ratio, including income, existing debt obligations, and proposed mortgage payments. Additionally, lenders consider credit score, employment history, and assets when evaluating an applicant’s financial profile.
Ideal Loan to Debt Ratio
Striving for the Ideal Loan to Debt Ratio
While acceptable ratios may vary among lenders, the general consensus is that a lower ratio is favorable. Most lenders prefer a loan to debt ratio below 36%, with mortgage payments typically accounting for no more than 28% of gross monthly income.
Calculating Loan to Debt Ratio
How to Calculate Your Loan to Debt Ratio
Calculating the loan to debt ratio involves dividing total monthly debt payments by gross monthly income and expressing the result as a percentage. This simple formula provides insight into an individual’s financial obligations relative to their income.
Tips for Improving Ratio
Tips to Improve Your Loan to Debt Ratio
For individuals with high loan to debt ratios, there are strategies to enhance financial health. These may include paying off existing debts, increasing income through additional employment or side hustles, and reducing unnecessary expenses.
Risks of High Ratio
Understanding the Risks of a High Loan to Debt Ratio
A high loan to debt ratio poses several risks, including limited borrowing capacity, higher interest rates, and potential rejection of mortgage applications. Additionally, it may hinder financial flexibility and increase vulnerability to economic downturns.
FAQs
- Can a high loan to debt ratio affect my mortgage approval?
- Yes, a high ratio may indicate financial strain and raise concerns for lenders.
- What steps can I take to lower my loan to debt ratio?
- Paying down existing debts, increasing income, and reducing expenses can help lower your ratio.
- Is the loan to debt ratio the same as the debt-to-income ratio?
- Yes, both terms refer to the proportion of income allocated to debt repayment.
- How often do lenders assess the loan to debt ratio?
- Lenders typically evaluate this ratio during the mortgage application process and periodically throughout the loan term.
- What is considered a good loan to debt ratio?
- A ratio below 36% is generally deemed favorable by lenders.
- Can I include non-debt expenses in the loan to debt ratio calculation?
- No, the ratio only considers debt-related obligations.

Loan to Debt Ratio
- No, the ratio only considers debt-related obligations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and managing the loan to debt ratio is essential for securing a mortgage and maintaining financial stability. By striving for a healthy ratio and implementing sound financial practices, individuals can enhance their chances of mortgage approval and achieve their homeownership goals.
Read More:>